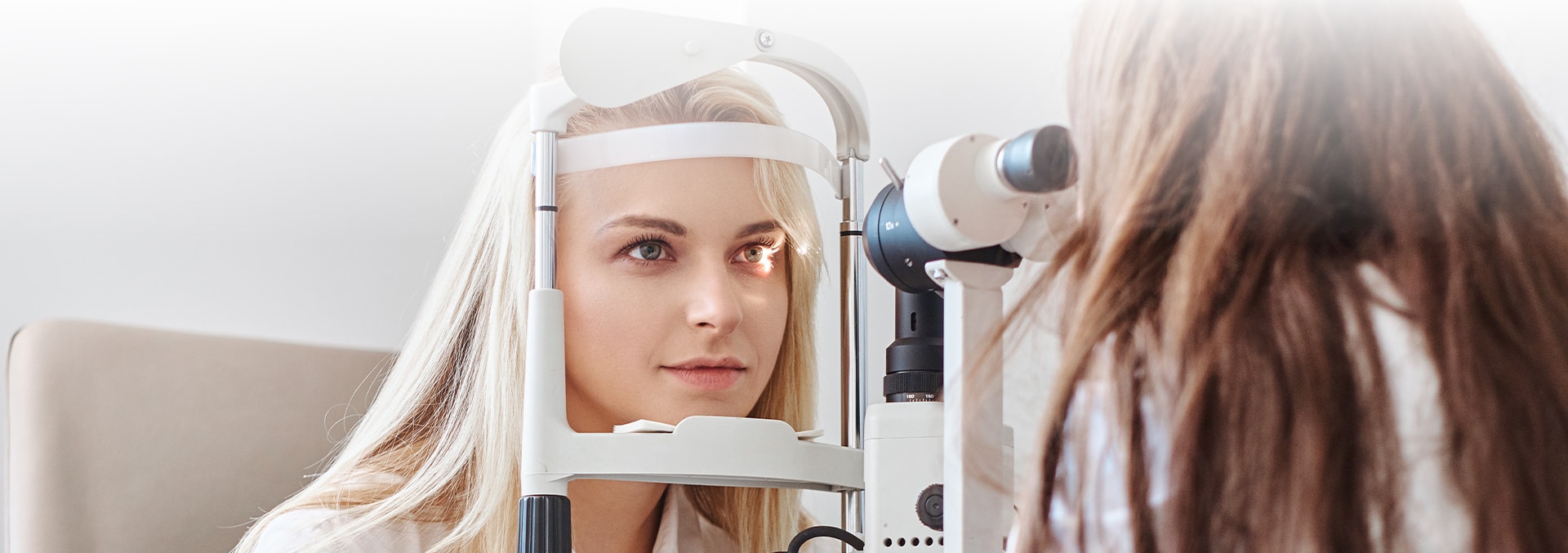
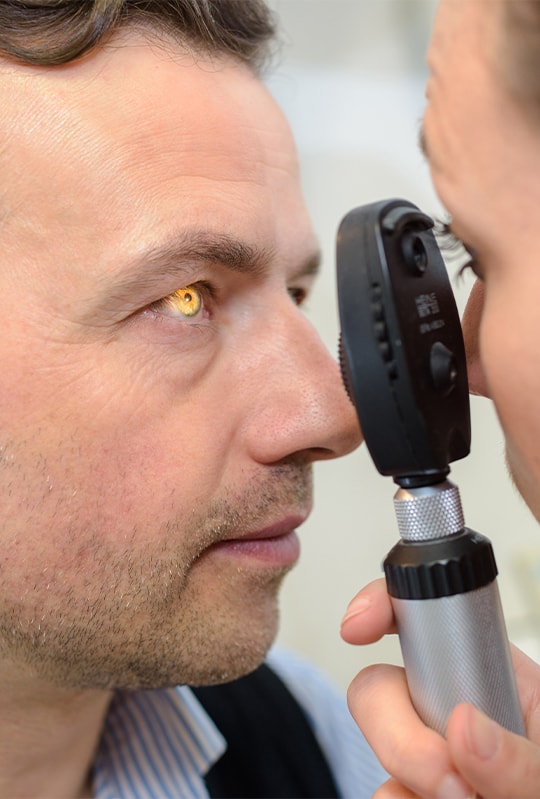
External Eye Exam
We check the position and movement of your eyes and the clarity of your iris and cornea.
Eye Muscle Test
You will be asked to follow an object to gauge your eye’s movement. We are checking for muscle abnormalities or uncontrolled movements.
Visual Acuity Test
This test will identify your visual acuity, as measured in a fraction (such as 20/20). The top number refers to your distance from the eye chart, usually 20 feet. The bottom number indicates the distance at which a person with normal eyesight could correctly read the line you read.
For example, 20/20 vision means that you can see objects clearly from 20 feet away that a person with normal vision could see clearly from 20 feet away. However, if your visual acuity is 20/50, the line you read correctly at 20 feet could be read with normal vision at 50 feet.
Refraction Assessment
This helps us determine the appropriate corrective lens prescription to give you the sharpest vision. We may use a state-of-the-art computerized refracting system to measure your eyes and estimate the prescription you need to correct a refractive error.
Perimetry Visual Field Test
A visual field test measures the area that your eyes can see without moving. This test identifies any problem areas or blind spots in your field of vision.
Slit-lamp Examination
Using a microscope and an intense light source, we examine your cornea, iris, lens, and your eye’s anterior chamber.
Tonometry
Tonometry is a tool that measures your internal eye pressure.
Retinal Examination
This test examines the back of your eye, including your retina, optic disc, choroid, and blood vessels.
If needed, we may dilate your eyes for this test. This will prevent your pupil from closing when exposed to light, allowing us to see the entirety of your eye interior. Your eyes will remain dilated for several hours after the exam and will be sensitive to light. You may not be able to go back to work immediately after the exam.